Design of Visualizations for Human-Information Interaction A Pattern-Based Framework
Book
Sedig, K & Parsons, P (2015). Design of visualizations for human-information interaction: A pattern-based framework. Morgan & Claypool Publisher. Synthesis Lectures on Visualization.
In this book we present a general, holistic framework that is intended to support visualization design for human-information interaction. The framework is composed of a number of conceptual elements that can aid in design thinking. The core of the framework is a pattern language—consisting of a set of 14 basic, abstract patterns—and a simple syntax for describing how the patterns are blended. We also present a design process, made up of four main stages, for creating static or interactive visualizations. The 4-stage design process places the patterns at the core of designers’ thinking, and employs a number of conceptual tools that help designers think systematically about creating visualizations based on the information they intend to represent
Conceptual Elements of Framework
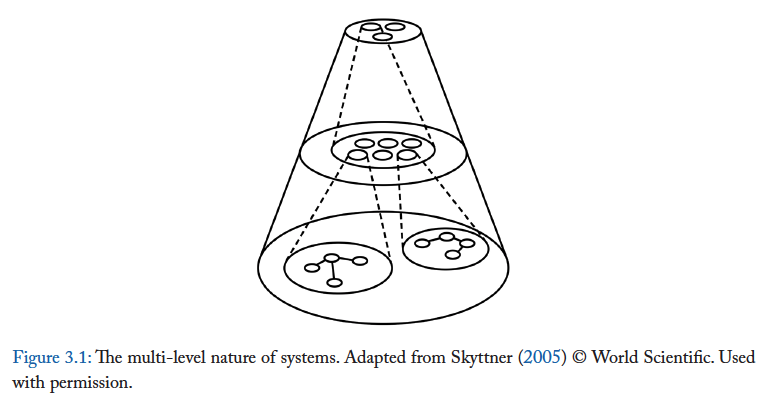
Systems Theory (concerned with the general properties of systems regardless of form or domain application)
Space (During design of visualizations, information is converted from an abstract form (statistics, data, i.e.) to a concrete (i.e. visual) form. Information Space - Representation Space. Metaphor useful for conceptual stage of design.
Information Space (not directly accessible and can only be accessed and interacted with through visualizations at the visually perceptible interface of a tool)
Information item are used to refer to only abstract things within an information space and not things that are visually perceptible in representation space (i.e. property, quantity, geolocation, measurement, datum, etc..)
Representation Space
Encoding vs. Representing
Encoding is concerned with conversion of information from one form to antoher, representation does not necessarily encode everything it represents.
Abstract vs. Concrete
Visual Structures - are configurations that suggest some type of organization of information
Visual Variables
Patterns
Blending of Patterns
Designers can blend different patterns to devise representational structures that have different organizational affordances.
Syntax
Human Information Interaction
Design Process
Applications of Framework
Quality of Life example
Genomics Example
Education Example